SHAKEN BABY SYNDROME

Have you ever shaken a baby, either in anger or because you thought it will make the baby happy?
Don’t ever do that! This can lead to serious and sometimes, permanent injuries, especially to brain. There is a term in medical for it, called “shaken baby syndrome”.
VIDEO
WHY DOES IT OCCUR IN BABIES?
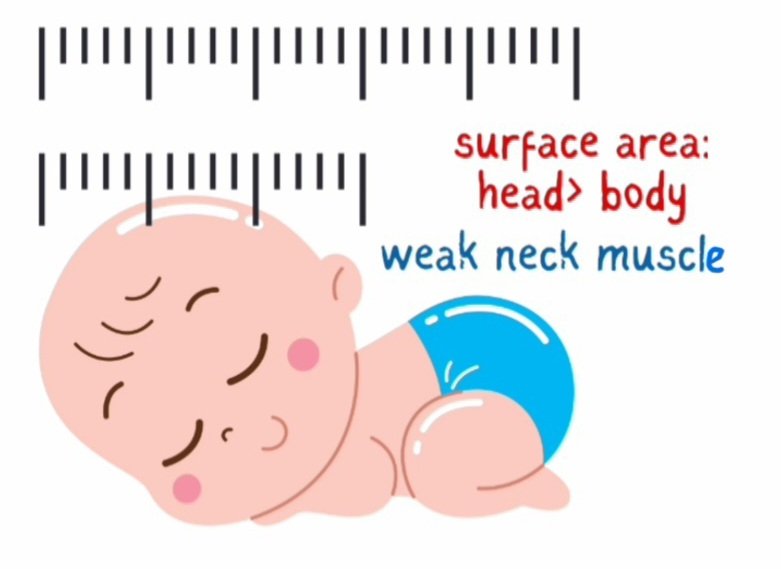
Babies have proportionately larger head in comparison to bodies. This proportion decreases as we age. The weak neck muscles have to support this large size head. Thus, shaking of a baby causes more movement of skull and brain with it. Also, the immature and growing brain of a child carries more risk of injury and permanent damage than an adult’s brain.
Age group: Its seen most commonly in infants lesser than 1 year of age, but has been reported in children up to 4 years of age.
WHAT CAUSES IT?
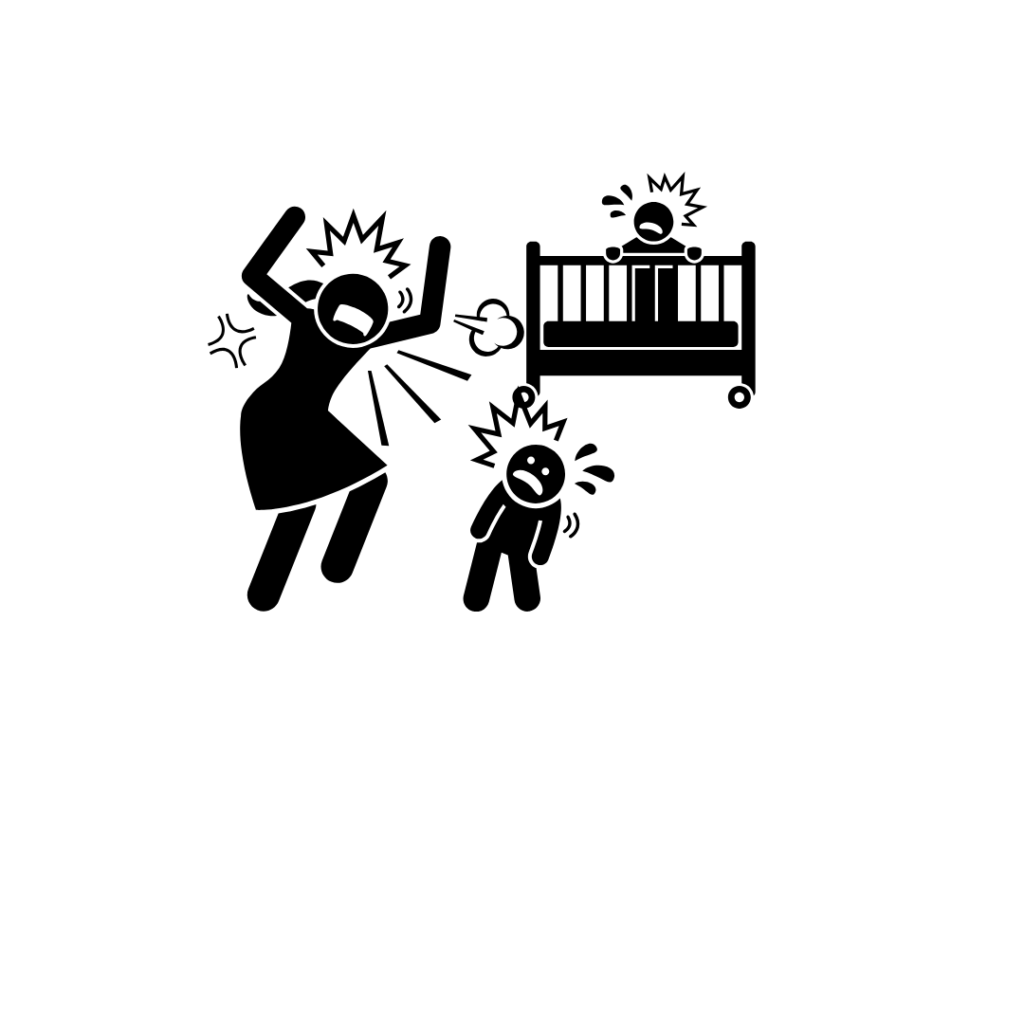

Its usually caused by mechanism in which baby’s head is moved too fast in various directions.
This is seen when a caregiver shakes the baby in anger or frustration, without realizing its impact. Rarely, some younger kid or adult, may shake the baby, as a part of play, where they think the baby is enjoying it.
HARMS OF SHAKING THE BABY
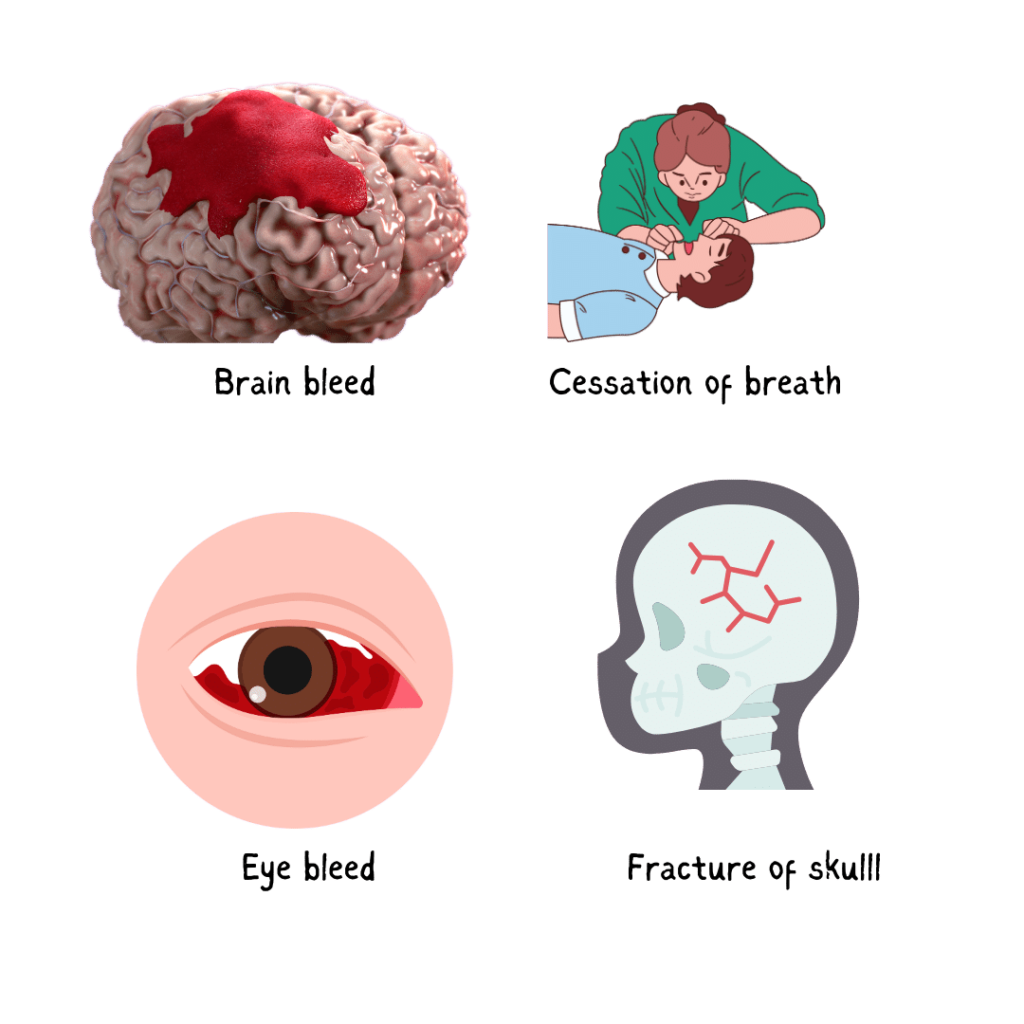
- Injury to any part of brain: Injury can occur to brain matter when the soft brain matter strikes against the hard bony skull it is confined within.
- Bleed in brain: Continuous violent to & fro movement can lead to tearing of blood vessels of brain.
- Cessation of breath: Brain controls the breathing centers in our body. Injury to these parts of brain can lead to temporary or permanent cessation of breathing. In the most serious form, it can lead to death on spot, too. Temporary cessation of breathing can also lead to lack of oxygen supply to brain, which may lead to permanent and irreversible damage to various parts of brain.
- Bleeding in eyes: Shaking can also damage blood vessels of eye. Most bleeds are seen in the inner layer of eye (called retina).
- Fracture of skull bone (or fracture of other bones of body), depending upon the type of assault or impact).
WHAT SYMPTOMS CAN BE SEEN IN THE BABY?
It mainly depends upon the area of brain injury. Some long lasting effect on brain, may manifest later as the child grows. Following are the common symptoms encountered:
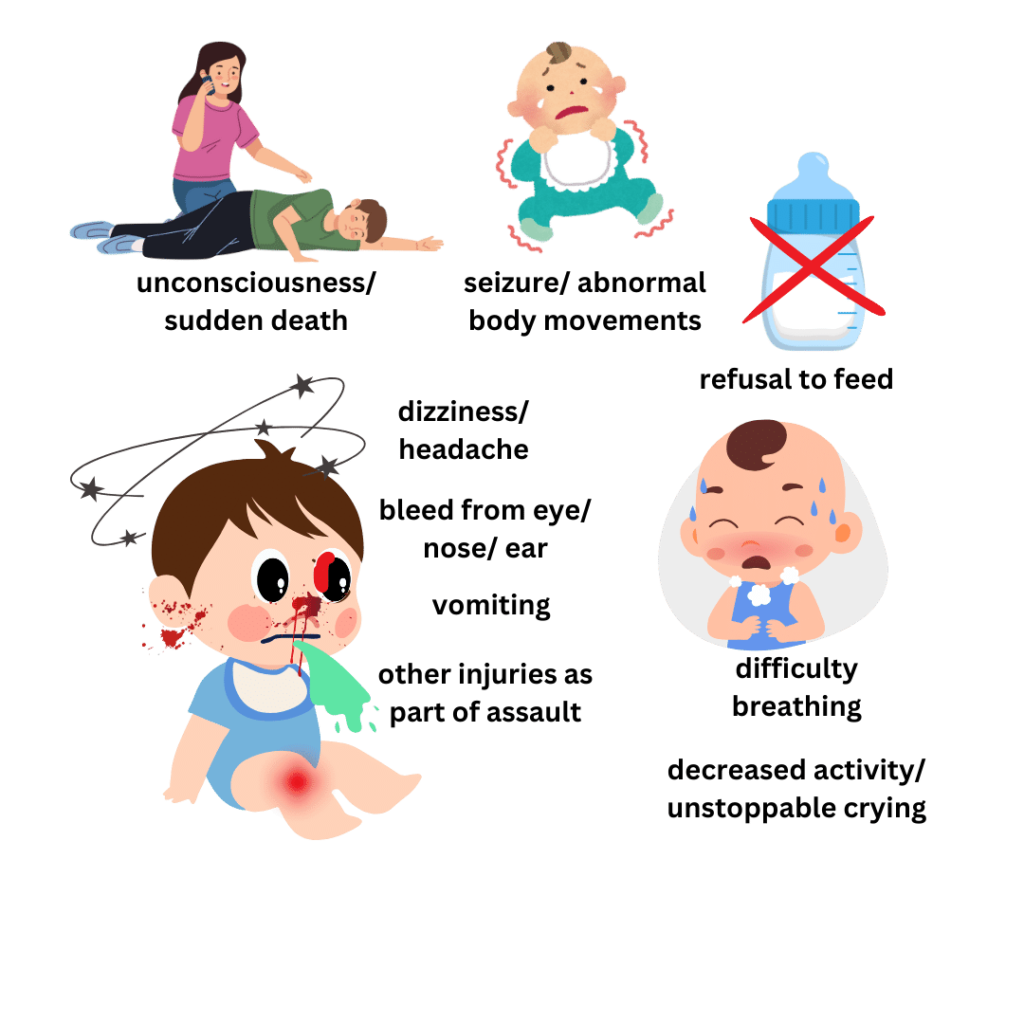
- Unconsciousness (fainting)
- Seizure or abnormal movements
- Decreased activity in a previous active baby
- Refusal to feed
- Growing head size
- Vomiting
- Elder baby may complain of headache, dizziness or vision difficulty. Sudden change in behavior in elder baby should also be noted.
- Bruises on head, around eyes, behind ears (or other body parts of body as a part of assault)
- Bleeding from nose or ears
- Eye bleed
- Fracture of other bone, as part of abuse.
DIAGNOSIS/ INVESTIGATIONS
If you spot any of above mentioned symptoms in your baby or suspect abuse, take the baby to the hospital. you can expect the following diagnostic procedure to be carried out:
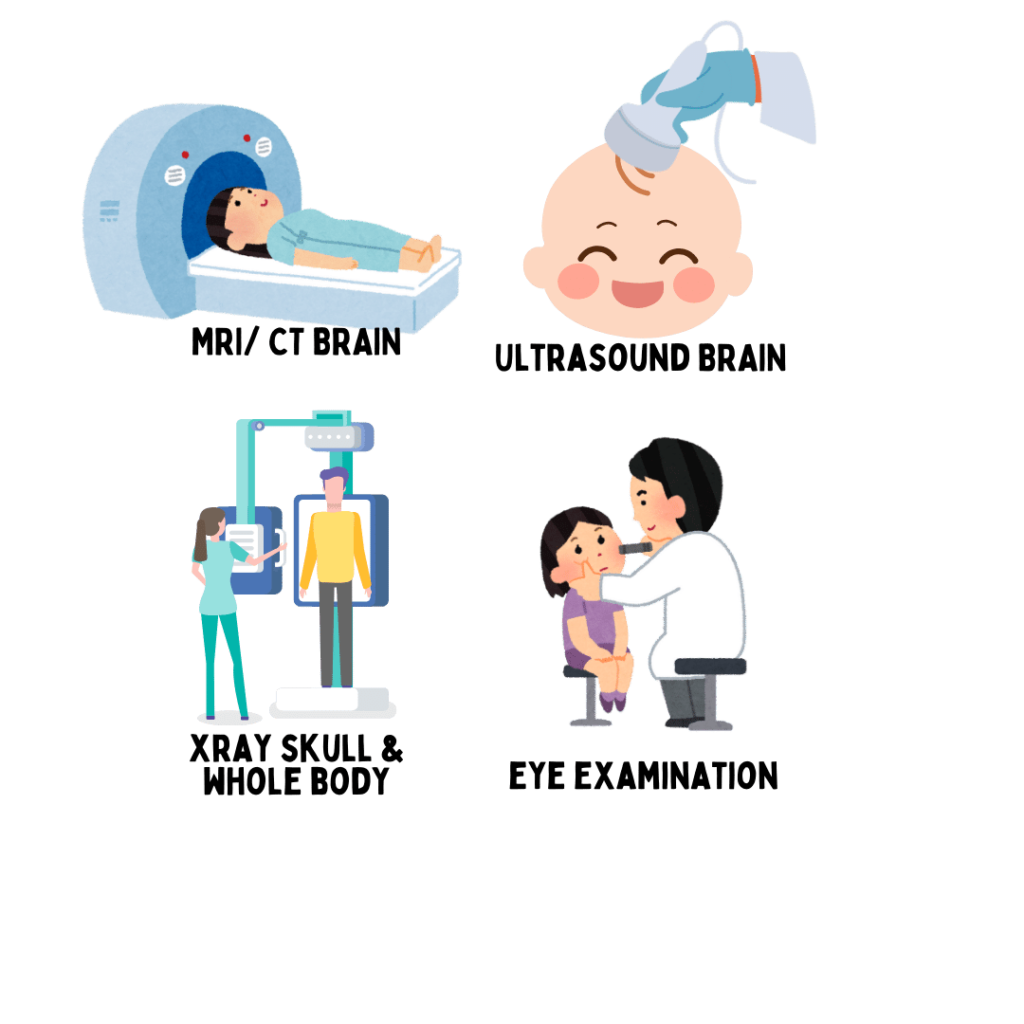
- Brain imaging : CT/ MRI of brain to look for bleeds or injury. Ultrasound of brain (possible in baby less than 1 year or till their skull bone is open).
- Eye examination: to look for eye bleed (retinal hemorrhage). This is a very common finding in cases of abuse, even when there is no bleed in brain.
- Skeletal survey: A whole body xray to look for injury in other bone or soft tissue, which can as a part of abuse.
- Blood examination: Usually done in severe cases, to look for the amount of blood loss.
TREATMENT
Once child is taken to hospital, further treatment depends upon the condition of child, severity of symptoms and findings in reports.

WAIT & WATCH: minor bleeds in brain can improve on its own and child may be watched with regular follow up with doctor.
SURGICAL REMOVAL OF BLEED: depending upon the place of bleed in brain, the amount of bleed and the symptoms caused by the bleed, urgent removal of collected blood may be needed.
BREATHING SUPPORT: If breathing is compromised, breathing support ranging from use of oxygen to ventilator support may be needed.
EYE BLEED: It resolves gradually, within few weeks, in most cases.
OTHERS: Any other supportive treatment as per the problem faced by the child will be provided. For example, blood transfusion (if there has been loss of too much blood) or treatment of fracture or pain, etc..
PREVENTION

If you feel overwhelmed or frustrated, put your child down. Remember, its okay to feel so.
- Take deep breaths and count backwards, till you feel relaxed.
- Talk to your friend, relative or healthcare.
- Ask for help.
- Hire a help, if feasible.
Never leave a child with someone you can not trust.
Always enquire or review a babysitter or daycare, before leeaving your child there.
Install a webcam.
Take the child to healthcare when in doubt.
NOTE: Remember, prevention is better than cure. All conditions may not be treatable. But it is a preventable condition.



